Pneumatic tools are essential in industries where precision, durability, and safety matter most. At the heart of many of these tools lies the air motor — a compact yet powerful device that converts compressed air into mechanical motion. Whether you’re in automotive repair, manufacturing, or heavy machinery maintenance, understanding how air motors work and where they shine can help you choose the right tool for the job.
What is an Air Motor?
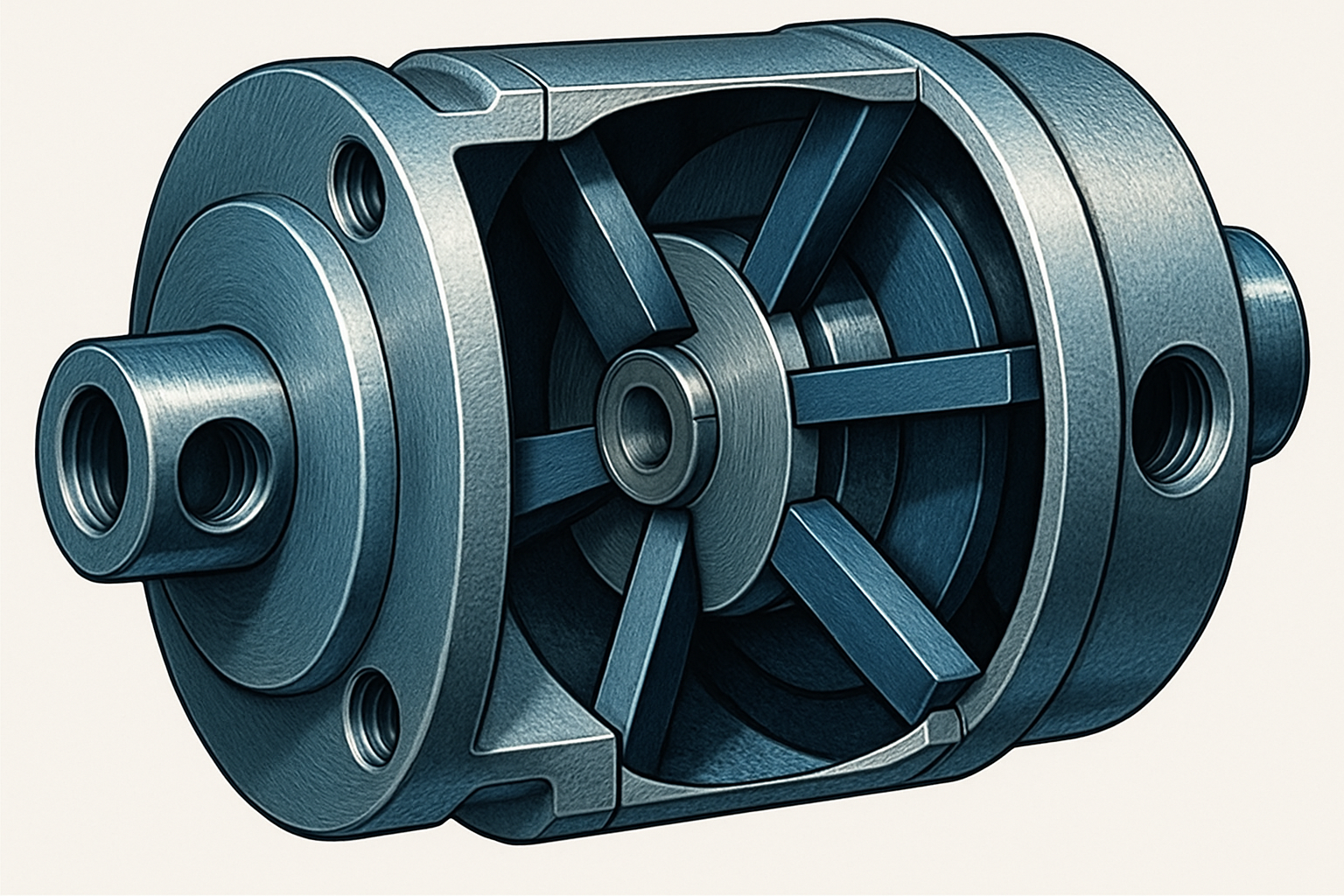
An air motor (also called a pneumatic motor) is a mechanical device powered by compressed air. Instead of using electricity, it harnesses air pressure to generate rotational or linear motion through mechanisms like pistons or vanes (Hydraulics & Pneumatics).
-
Piston Air Motors: Use reciprocating pistons to create motion.
-
Vane Air Motors: Use rotating vanes that expand with compressed air to produce torque.
👉 Learn more about how Soartec designs and tests professional pneumatic tools.
How Do Air Motors Work?
The basic principle is simple: compressed air enters the motor chamber, where differences in air pressure drive movement. The output can be rotation (ideal for impact wrenches, grinders, and drills) or linear motion (useful for actuators and automation).
A unique feature of air motors is their instant torque. Unlike electric motors, they don’t require a warm-up period and can start under load immediately.
Benefits of Air Motors

-
Durability & Reliability – Simple structure makes them highly durable, even in tough environments like mining, oil & gas, and automotive workshops.
-
Safe in Hazardous Environments – No risk of sparks or fire, making them perfect for flammable or explosive settings (Atlas Copco).
-
Lightweight & High Power Density – Provides high torque with a lighter build, ideal for heavy-duty impact wrenches like Soartec’s WS-211T-6 Air Impact Wrench.
-
Low Maintenance – Fewer moving parts and resistance to overheating allow for continuous high-frequency use.
Limitations of Air Motors
-
Dependence on compressed air supply.
-
Complex control systems may be required for speed and torque regulation.
👉 For industries with stable compressed air systems, however, these trade-offs are minor compared to their benefits.
Best Applications of Air Motors
Air motors are used across many industries, including:
-
Automotive Repair – Impact wrenches, drills, and sanders. Explore Soartec’s automotive pneumatic tools.
-
Heavy Machine Maintenance – Large torque applications in construction and mining.
-
Oil & Gas Industry – Safe in explosive environments where electric motors are risky.
-
Manufacturing & Assembly Lines – Ideal for automation systems requiring repetitive precision.
-
Railway Maintenance – For bolting, cutting, and grinding under rugged conditions.
For example, Soartec’s WS-406 Air Diesel Injector Puller demonstrates how air motors power specialized tools for diesel engine servicing.
Air Motor vs Electric Motor
When deciding between an air motor and an electric motor, consider:
-
Air Motor Advantage: Lightweight, safe in hazardous areas, and ideal for high-frequency use.
-
Electric Motor Advantage: Higher efficiency and doesn’t require compressed air.
In industries where safety, portability, and high torque-to-weight ratio are critical, air motors remain unmatched.
Final Thoughts
Air motors are the hidden powerhouse of pneumatic tools, enabling professionals worldwide to work safely, efficiently, and reliably. From automotive workshops to industrial assembly lines, they play a key role in keeping operations running smoothly.
If you’re looking for durable, high-performance pneumatic tools, explore Soartec’s product catalog and discover why we are trusted by professionals across the globe.